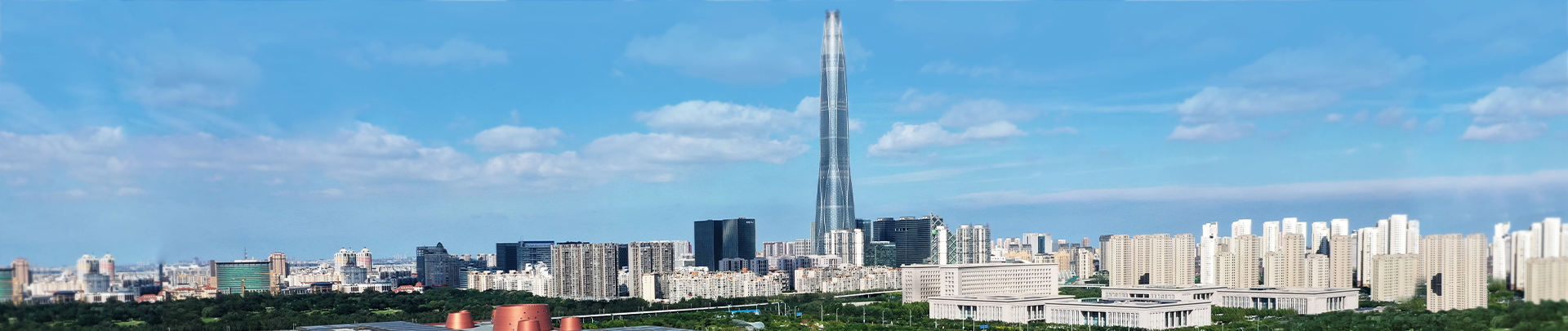
Tianjin Lays Out Plans for Economic Growth

Tianjin municipal government’s information office held a press conference on July 30 to showcase the strides the city has made in promoting high-level economic openness.
During the briefing, an information office official said that, since the beginning of this year, Tianjin has focused on the central task of economic development and has driven comprehensive reforms with the coordinated development of Beijing, Tianjin and Hebei as its strategic guide, thereby solidifying its status as a robust open economy.
According to the information office, in the first half of this year, Tianjin achieved significant milestones in foreign trade, with total imports and exports reaching 400.3 billion yuan ($55.39 billion). The number of foreign trade bodies engaged in import and export activities reached 10,800, representing an 8.6 percent increase on 2023 and setting a new record.
Cross-border e-commerce witnessed a notable 26.6 percent surge in trade volume, while the export of used cars nearly tripled to almost 4 billion yuan. Currently, Tianjin is home to more than 290 Fortune 500 companies, with major projects such as Airbus, Novo Nordisk and SMC progressing rapidly.
At the press conference, Sun Jiannan, director of the Tianjin Commerce Bureau, outlined the bureau’s forthcoming priorities, with plans in place to establish a trillion-yuan foreign trade powerhouse.
Initiatives planned include creating a national import trade promotion innovation demonstration zone and piloting programs like bonded fuel oil refueling for international ships, bonded remanufacturing of auto parts, and the importation of remanufactured products in strategic sectors.
Efforts will also focus on making it easier to export used cars, promoting trade in intermediate products, and supporting enterprises to participate in major international exhibitions. In addition, a comprehensive pilot zone for cross-border e-commerce will be developed as part of a three-year action plan aimed at high-quality sectoral development, alongside bolstering support for overseas warehouse enterprises.
Concurrently, Tianjin will intensify its marine economic strategies, aiming to deepen integration across ports, industries and urban areas. The plans include establishing a hub for the allocation of bulk commodity resources, transitioning port trade from basic import-export activities to value-added exchanges, and extending industrial chains and value-added links for key traded goods such as high-end agricultural produce, metals, frozen products, automobiles and grain.
Smart port initiatives are set to accelerate, accompanied by the expansion of international trade “single window” services throughout the trade chain. Tianjin also plans to optimize designated supervision sites and open ports, implementing streamlined customs clearance measures to enhance overall port service capabilities.










 津公网安备 12019002000128号
津公网安备 12019002000128号

