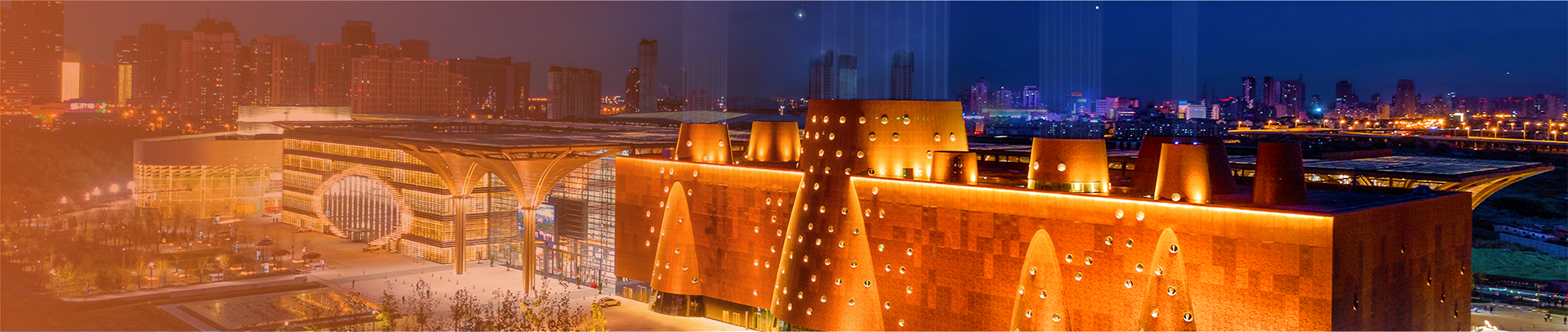
Features
TEDA Embraces a Promising Future in a Blueprint of Building International Consumption Center Cities
Nangang Industrial Zone, a Land Leads to Infinite Future
Low-carbon Development for a Beautiful TEDA
TEDA’s National-Level Demonstration Bases for Neo-Industrialization
Interview | 77-million-dollar Investment from Time-honored Partner
The 5th WIC to Be Held in Tianjin with 6 New Highlights
Visit TEDA on Haihe River Cruise
Tianjin Port, a World-class Port
Foreign-funded Enterprises Felt Confident about TEDA with a Stronger Presence Here
The Best Way to Enjoy the Spring Festival in TEDA
Headquarters Gathering in TEDA
Pharmaceuticals & Big Health
Interview|15-year Friendship, Eramet Confident in TEDA’s Investment Environment
Ever-upgrading Business Makes Life Better in TEDA
2021 TEDA Auto Forum is Coming to Town
Government and Business Leaders Sharing Insights about the Future of Auto Industry in TEDA
NSCC-TJ Fuels up S&T Innovation in TEDA
TEDA’s Annual Appointment with the CIIE
A Glance at International Buildings in TEDA
TEDA, a New Magnet for Commercial Factoring
A Snapshot of Innovative Products from TEDA
Hightlights of 2021 in TEDA
Voice of TEDA | Presenters from TEDA Administrative Commission
A Solid Firewall for Pandemic Prevention & Control Gains More Trust for TEDA
A Better TEDA Seen by More
TEDA Elements in the Beijing 2022 Winter Olympic Games
Foreign Enterprises Deeply Involved in TEDA with Robust Momentum
Smart City Initiative for a Better TEDA
From a Deserted Salt Pan to the Heart of Binhai-the Code of TEDA’s Growth
Foreigners Living in Tianjin Know Everything
The 6th WIC Held in Tianjin
TEDA: Technological Innovation Leads Green Manufacturing
2022 TEDA Auto Forum is Coming
The 2022 TEDA Auto Forum——Government and Business Leaders Sharing Insights over the Development of China’s Auto Industry
New Cultural, Commercial and Tourism Highlights Empowering TEDA’s High-quality Growth
TEDA Elements Shine at the 5th CIIE
Generating Core Revenue over 150 Billion Yuan, Eight Scenarios Embody Achievement of TEDA’s Digital Economy Growth
TEDA Investment Promotion Milestones in 2022
A Closer Look at TEDA’s Industrial Chains: Biomedicine
Bullish on TEDA, Foreign Investors Redoubling Investment as Votes of Confidence
TEDA Industrial Tour and Science Popularization Tour is Waiting for You
A Closer Look at TEDA’s Industrial Chains: High-end Machinery
TEDA Reinforces its Presence in Europe
Tianjin Hosts the 7th World Intelligence Congress: TEDA Shines in Regional Intelligent Development
Binhai Fund Town Creates the TEDA Model of Industry-Finance Integration
Embracing Davos: TEDA Opens Its Doors to the World
TEDA Ready to Customize Special Tour Routes for the Davos Forum
A Closer Look at TEDA’s Industrial Chains: Automobile
Looking back into the Industrial History of Tianjin: TEDA Composes a New Chapter as an Industrial New City
Government and Enterprise Leaders Gather at the 2023 TEDA Auto Forum to Shape the New Future of the Industry
2023 TEDA Auto Forum——Embracing a New Future with High Quality
Understand How European-Funded Enterprises Intensify Presence in TEDA from Four Key Words
TEDA Welcomes National Day with Continuous and Exciting Events
A Closer Look at TEDA’s Industrial Chains: Integrated Circuit
International Chinese Course Begins – Witness How “Laowai” Learn Chinese in TEDA
Digitization Makes TEDA a Leading Place for Digital Healthcare
TEDA Investment Milestones in 2023
In the Prime of Life - Opening Statement for Series Report “Growing with Our Investors” Marking the 40th Anniversary of Tianjin Economic-Technological Development Area
TEDA’s 40th Anniversary——A Story of Breakthroughs and Regional Growth in Four Decades
Growing with Our Investors—Looking back on TEDA’s Early Days (Part I)
Growing with Our Investors—Looking back on TEDA’s Early Days (Part II)
New Quality Productive Forces in TEDA
Foreign Investment Upgrades from Manufacturing Plants to R&D Centers in TEDA
Growing with Our Investors—TEDA Striding Ahead (1990-1994) (Part I)
Growing with Our Investors—TEDA Striding Ahead (1990-1994) (Part II)
Fruitful Results in TEDA at World Intelligence Expo 2024
Growing with Our Investors—Serving Investors in an All-round Way and Building a Beautiful TEDA (1995–1999) (Part I)
Focusing on TISIE & Maritime Day; Shipping to the Future Development
Embracing Marine Economy: TEDA to Promote Ports, Industries, and Cities Integration
Growing with Our Investors—Serving Investors in an All-round Way and Building a Beautiful TEDA (1995–1999) (Part II)
TEDA Smart Environmental Protection Platform: Empowering Green Development
Building on the Extraordinary Twenty Years & Working Together for a Shared Future—2024 International Forum (TEDA) on Chinese Automotive Industry Development Is Coming
2024 TEDA Auto Forum: Leading Think Tank Drives Automotive Industry
Growing with Our Investors—Striving Forward to Build a New Type of Modern Industrial Park (Part I)
Hi Fun in TEDA—TEDA Welcomes Global Tourists on National Day Holiday
Growing with Our Investors—Striving Forward to Build a New Type of Modern Industrial Park (Part II)
Growing with Our Investors—TEDA Takes Great Strides with GDP Crossing the 100-Bln Threshold (2005-2009) (Part I)
Growing with Our Investors—TEDA Takes Great Strides with GDP Crossing the 100-Bln Threshold (2005-2009) (Part II)
Growing with Our Investors—TEDA Sets Sail for New Horizons in Its Prime (2010-2014)
Growing with Our Investors—TEDA Takes New Opportunities to Forge Ahead (2015-2019)
Growing with Our Investors—TEDA Writes New Chapter for Future in 40th Anniversary (2020-2024)
Series Report “Growing with Our Investors” Marking the 40th Anniversary of Tianjin Economic-Technological Development Area
2024 Milestones of INVEST IN TEDA
4 Highlights of TEDA’s Investment Achievements in 2024
TEDA’s Cultural & Tourism Feast Awaits You to Celebrate Chinese Spring Festival!
TEDA’s Facilitation for Expats & Foreign Companies
Guide for Expats & Foreign Companies in Tianjin and China
When I Ask DeepSeek about TEDA…
Foreign Investors Foster New Engines for Higher-end, Smarter, and Greener Development in TEDA
TEDA Remains Top Destination for Multinational Investment, China Development Forum Ignites Investment Momentum
The Rise of TEDA’s New Chemical Materials Industry: Insights from the China Development Forum
10th Anniversary of Tianjin Pilot FTZ Central Business District
Insights from China Development Forum: TEDA’s Innovative Practices in Modern Service Industry
Amazing Ecology! TEDA “Novo Nordisk Cup” Bird Photography Competition Winners Announced
Decoding the Robust Ascent of TEDA’s Low-altitude Economy
Tianjin Binhai New Area Investment Promotion Conference Held in Beijing -- Why Industry Leaders Choose TEDA
A Closer Look at 2025 Tianjin International Shipping Industry Expo -- Why TEDA Draws Global Attention?
Multinational Giants Gather in Tianjin,Davos Strategic Partners Shine in TEDA
Measures for Promoting Green and Low-Carbon Development in the Tianjin Economic-Technological Development Area (TEDA)
The 2025 Sustainable Development (ESG) Report of Tianjin Economic-Technological Development Area(Chapter I. The TEDA Model of Green Transition)
The 2025 Sustainable Development (ESG) Report of Tianjin Economic-Technological Development Area(Chapter II. Common Prosperity of Industries and Local Community)
The 2025 Sustainable Development (ESG) Report of Tianjin Economic-Technological Development Area(Chapter III. Innovative Initiatives Sets Benchmark for High-Efficiency Growth)
The 2025 International Forum (TEDA) on Chinese Automotive Industry Development to Kick Off Soon
2025 International Forum (TEDA) on Chinese Automotive Industry Development Releases Think Tank Consensus, Outlining Four Major Directions for the Automotive Industry
Political and Business Leaders Gathered at the 2025 International Forum (TEDA) on Chinese Automotive Industry Development for the Blueprint of the Automotive Industry in the 15th Five-Year Plan Period
Ocean Carnival, Ancient Town Charm, Cultural Feast: TEDA Invites You to Enjoy the 2025 National Day Holiday
Private Economy Booms in Both Scale and Quality When TEDA Advances High-End, Intelligent, and Green Industrial Development
TEDA’s Aerospace Industry Takes Off with Speed and Momentum
Highlights of the TEDA Forums 2025
2025 Milestones of INVEST IN TEDA
Tianjin Introduces 98 Measures to Advance High-level Opening-up of Pilot Free Trade Zone
Application Scenarios in TEDA (Intelligent Technology Industry)
The 2026 Spring Festival Cultural and Tourism Feast Awaits you in TEDA: Ocean Resort Lantern Show, Ancient Town Fair, and Cultural Gatherings Unveiled












 津公网安备 12019002000128号
津公网安备 12019002000128号

